The flowchart below summarizes the causes of infertility in men. It may seem too complex at the beginning. But don’t panic! I’ll walk you through all these causes, using simple language.
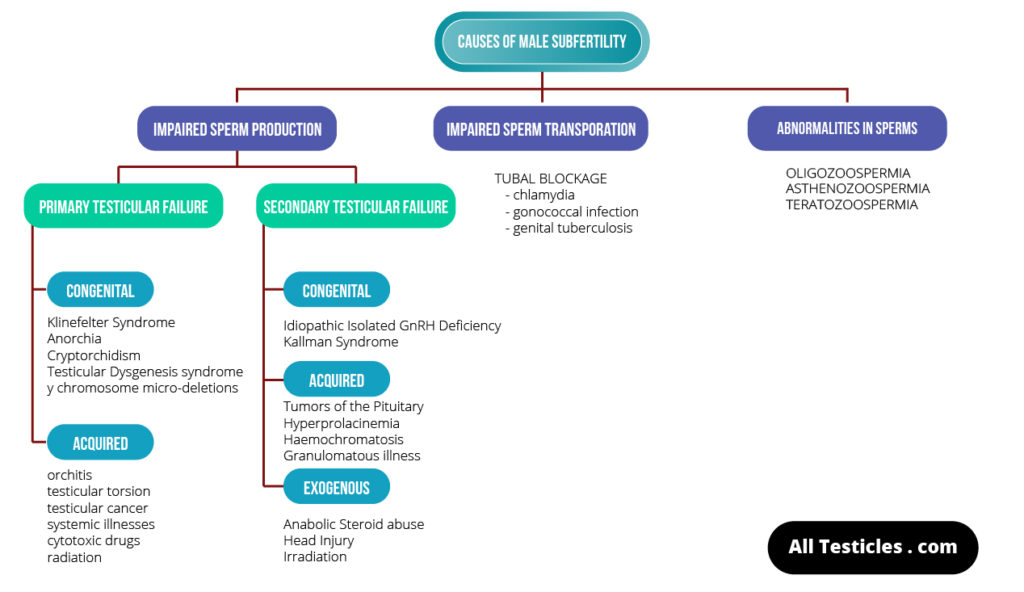
Please use the above flow chart as a guide when you read the article. Also, don’t forget to take notes, as this is going to be a lengthy but very informative discussion on Causes of infertility in men.
In this article we will mainly answer these three topics, with special weight being given to the third topic (causes of infertility in men).
- How is Male Infertility Diagnosed?
- Importance of knowing the causes of infertility in Men
- Causes of Infertility in men- in depth discussion
Diagnosis of Male Infertility
There are so many causes of male infertility. Unfortunately, the causes of male infertility are not recognized early, and only identified when the couple realize they have a difficulty in conceiving a child and seek medical help from an Urologist, Andrologist or a Gynecologist.
When the couple meets the specialist, the doctor will take a history, perform a thorough medical examination, and run some investigations to confirm the sub fertility and to identify the causes of infertility in men and women.
Is knowing the cause of infertility important for treatment?
Since there are number of causes of male infertility, there’s no single treatment option which works for everyone. Your doctor will have to find the exact cause of infertility (or exclude other causes to find possible differential diagnoses) and offer you matching treatment options. So it is vital to know that there are many causes of infertility in men. We’ll go through them one by one in this article.
Why do men become infertile: Three main causes of infertility in men
We can categorize all the causes into three main subtypes. Then it will be easier to understand them in detail.
- Reduced or absent production of healthy sperms
- Problems in transportation of sperms
- Structural and functional abnormalities of sperms
Okay so let’s start the discussion with the first cause!
1. Male sub-fertility due to reduced or absent production of healthy sperms
Let’s see what are the causes for the reduced or absent production of healthy sperms.
- Sperm production
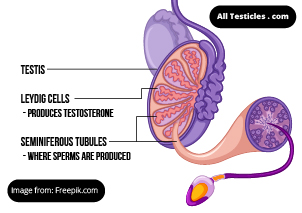
Image Attribution: Freepik.comSperms are the male reproductive cells. They look like tiny tadpoles under the microscope. Sperms are produced in the testicles by cells known as Leydig Cells.
For the production of sperms, there must be a hormonal trigger. One such hormone is Testosterone, which is produced in the Testis itself. But the hormonal mastermind of sperm production are not the testicles, it’s the Brain!
There are two glands known as hypothalamus and pituitary in the brain.
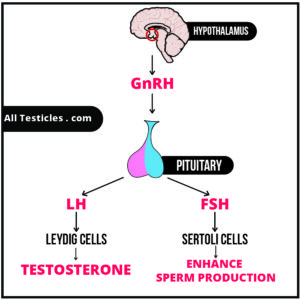
- Hypothalamus secrets a hormone called GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone).
- GnRH stimulates Pituitary to secret FSH (Follicular stimulating hormone) and LH hormones (Luteinizing hormone)
- LH hormone stimulates the Leydig cells in the testis, to produce Testosterone
- FSH hormone stimulate the a cell group called sertoli cells which supports the production of Sperms.
- Testosterone also stimulates sperm production.
To produce healthy sperms male partner must have at least one properly functioning testis. So the absence of healthy testicles and/ or the impairment of hormone production in the body can lead to male subfertility.
Now that we know the hormonal axis of Sperm production, it is the best time to learn how different causes lead to male infertility
Impaired hormone production leading to Male infertility
Let’s see how the impairment hormone production can lead to Male infertility. This hormonal imbalance can occur due to the disorders in the,
- Testicles themselves (Primary Testicular Failure)
- Abnormalities affecting other hormonal systems (Secondary Testicular Failure) such as
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland
- Adrenal Glands
- Thyroid Gland
- What is Primary testicular failure?
Primary testicular failure is a condition where testes fail to produce adequate amounts of Testosterone (Endocrine Failure) or where it fails to produce healthy sperms despite adequate hormonal support (Exocrine Failure). Primary Testicular failure is also known as hyper- gonadotropic hypogonadism (Ignore this technical term for the moment. I’ll explain them in a future article)
So what are the causes for Primary Testicular Failure?
Well, they can be categorized again as
- Congenital Causes
- Acquired Causes
Congenital causes of Primary testicular failure
• Klinefelter syndrome

This is a genetic condition affecting males. In normal males, they have a single pair of sex chromosomes. They are X and Y chromosomes. In Klinefelter syndrome, there are three sex chromosomes XXY. This chromosomal abnormality leads to male infertility.
• Anorchia
Anorchia is the absence of testicles. Since Testes is where sperms are produced, it is not possible for Anorchia patients to be fertile.
• Cryptorchidism
At the beginning of fetal development, testicles are located inside the abdomen. At the end of the fetal development, testicles descend into the scrotum, where they are normally located in adults. When one or both testes fail to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum, it is known as cryptorchidism. It can result in male infertility.
• Testicular Dysgenesis Syndrome
Okay, So Testicular Dysgenesis Syndrome (TSD) is a group of disorders believed to have a common origin in the fetal life. It is characterized by the presence of,
- Male genital track malformations like hypospadias (opening of the urethra on the underside of the penis), cryptorchidism
- Testicular Germ Cell Cancer
- Production of poor quality semen
- Impaired production of testosterone
• Y chromosome micro deletion
This is another genetic condition affecting males. Like I explained above, males have two Sex Chromosomes known as X & Y. Deletion of the Y chromosome is one genetic condition which can cause infertility in men.
Acquired cause for Primary testicular failure
- Orchitis
Orchitis is the inflammation of the testis. Inflammation of the tesits can occur due to bacterial such as chlamydia infection, gonorrhea, and or viral infections like mumps. Mumps is a viral infection that infects the salivary glands known as parotid glands. It can also affect the testicles and lead to the development of mumps orchitis.
- Testicular torsion
Testicles are located inside a sac known as the scrotum. Blood supply to these testicles run through a tube known as the spermatic cord.
This spermatic cord can be rotated and twisted. This is known as testicular torsion.
It is an emergency condition because the cut off of the blood supply to the testicles can lead to permanent damage to the testicles.
Testicular torsion present with unbearable sudden pain and swelling of the scrotum/testicles. If you experience these features, you should immediately go to the hospital. If the viability of the testicles fails, it will lead to male subfertility and might require the removal of the dead testis (orchiectomy).
- Testicular Cancer-
The most common type of testicular cancer is germ cell tumors. Germ cell tumors can be sub-divided into seminomas and non-seminomas.
Testicular cancers can present with a lump in the scrotum, swelling of the scrotum or scrotal pain. When there is cancerous cells invade the sperm producing areas of testis (seminiferous tubules), the sperm production gets impaired.
- Systemic illness-
The various kinds of diseases affecting the body can lead to primary testicular failure.
- Cytotoxic drug therapy-
Cytotoxic drug therapy is used in the treatment of various cancers. These drugs act on cancer cells and prevent the cell division. This helps to destroy the cancer cells and reduces the progression of cancer.
But unfortunately, these cytotoxic drugs can act on normal body cells that divide fast like skin, hair, gastrointestinal tract and reproductive cells. When these cytotoxic drugs act on testicles normal division of cells gets impaired leading to reduced production of sperms.
- Radiation-
Radiation is used as either therapy or an investigation method. Radiation therapy is used in the treatment of cancers. Excessive radiation in either way can lead to primary testicular failure.
- What is Secondary Testicular Failure (hypothalamic pituitary failure)?
There are two glands known as hypothalamus and pituitary in the brain. Hypothalamus produces GnRH, and Pituitary produces FSH and LH. When these two glands fail, the testicles also fail due to the lack of hormonal stimulation. This is known as the Secondary Testicular Failure. By checking the serum FSH and LH hormone levels, this hypothalamic pituitary failure can be identified. The technical term for Hypothalamic Pituitary Failure is Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (Again, Please ignore the term! I’ll explain them in future)
- What are the causes for hypothalamic and pituitary failure?
Hypothalamic and pituitary failure can occur due to,
- Congenital abnormalities
- Acquired abnormalities
- Exogenous factors
Now let’s discuss these categories in detail.
- Congenital abnormalities leading to Hypothalamic and Pituitary Failure?
The main known congenital abnormality is Isolated GnRH deficiency. Well, we already know that Hypothalamus produces the GnRH hormone. But it also produces many other hormones as well. But in this condition, all the hormones are produced normally except for the GnRH. That’s how this condition got the name “Isolated GnRH deficiency”. So why would someone develop Isolated GnRH deficiency?
- There’s a known syndrome called Kallmann’s syndrome. These patients will have impaired smell sensations in addition to the GnRH deficiency.
- If the smell sensation is normal, then we call the condition “Idiopathic” Isolated GnRH deficiency. (In Medicine If we don’t know the exact cause; we just label them as Idiopathic!)
- What is Idiopathic Isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
In this condition, there is an impairment of GnRH hormone production in hypothalamus. In the absence of stimulation of GnRH, Pituitary gland produces only small amounts of FSH & LH hormones. Ultimately due to the inadequate hormonal support, testicles produce only fewer amounts of Testosterone and Sperms.
Since testosterone is essential to attain the puberty, these patients may have delayed puberty & may show lack of secondary sexual characteristics.
- What is Kallmann syndrome?
It is a rare genetic disorder. There is a delay or absence of signs of puberty in people with Kallmann syndrome. Also, they have an abnormality in sense of smell.
People with Kallmann syndrome have poorly developed sexual characteristics, lack of development of their testicles, small sized penis (micropenis) and cryptorchidism (undescended testis) like features.
- Acquired abnormalities leading to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Acquired abnormalities are conditions that occur after birth. Let’s talk about some important acquired causes.
- Tumors of the pituitary or hypothalamus
- Hyperprolactinemia,
- Granulomatous illness
- Haemochromatosis
- How can tumors of the pituitary lead to male subfertility?
Tumor cells divide faster than the normal cells. This can cause compression and destruction of the normal pituitary gland. It will result in impaired hormone production from this gland.
The most common type of pituitary tumor which causes infertility in men is Pituitary adenoma. There are two types of pituitary adenomas. They are,
- Microadenoma (less than 10mm diameter)
- Macroadenoma (more than 10mm diameter) : this is the type that can cause compression and destruction of tissues in the pituitary gland.
When there is a destruction of normal tissues in the pituitary gland, the production of FSH and LH hormones get impaired. FSH is the hormone that stimulates the testicles to produce sperms and LH is the hormone that stimulates testicles to produce testosterone hormone. As a result, sperm production and testosterone level in the body get reduced.
Hyperprolactinemia.
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition in which there is a high level of prolactin in the blood. Prolactin is a hormone produced in the pituitary gland. A common cause for hyperprolactinemia is a prolactin-secreting tumor in the pituitary gland known as a prolactinoma.
Let’s see how this hyperprolactinemia can leads to male subfertility.
High levels of prolactin have a negative influence on hypothalamus and in turn, it decreases the release of FSH and LH hormones into the blood. As FSH and LH are needed for sexual development, hyperprolactinemia can be a cause of infertility in men.
Haemochromatosis
Haemochromatosis is a condition where there is an increased iron levels in the body. This increased iron can be deposited in the various organs of the body. One such organ is the pituitary gland. When iron is deposited in the pituitary gland, it impairs its normal function. So the production GnRH hormone is also reduced.
- Exogenous factors leading to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Exogenous factors that lead to male subfertility include,
- Excessive use of anabolic steroids
- Head injury
- Irradiation
Male sub fertility due to anabolic steroids
Anabolic steroids usually use by bodybuilders and professional athletes. But its recreational use has increased with time. These anabolic steroids have similar properties to testosterone hormone.
When anabolic steroids are administrated into the body in excessive amounts, the pituitary is tricked to believe that there are high levels of testosterone in the body. So decreases the GnRH hormone production to minimize Testosterone levels.
Head injury
Hypothalamus and Pituitary glands can be damaged with head injury. As we have discussed many times, any damage to hypothamalo-Pituitary-Testis axis can lead to male infertility.
Head and neck irradiation
In the treatment of head and neck cancers, irradiation is used. It can damage the healthy tissues in the pituitary and the hypothalamus. So sex hormone production decreases and it will result in low level of testosterone in the body and impaired sperm production.
2. Male subfertility due to problems of transportation of the sperms
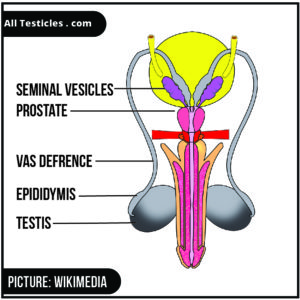
The male reproductive system consists of internal genital organs and external genital organs.
External genital organs include the penis and the scrotum.
Testicles, epididymis, vas deference and accessory gland are organs of internal genital organs.
Sperm production, also known as spermatogenesis, occurs in the seminiferous tubules in the testicles. These sperms are then transported into the epididymis.
Concentrated mature sperms are carried through the tube known as Vas deferens to the ejaculatory ducts.
There are three accessory glands. They are seminal vesicle, prostate gland and bulbourethral gland. The nutritious supply to the sperms is provided by fluids produced in these accessory glands. And this fluid also lubricates the duct system.
In the ejaculation, sperms come out from the ejaculatory duct through the opening of the penis.
When there is a blockage in the duct system or a damaged duct system is present, sperms cannot be transported properly.
How can the tubes get blocked?
3. Male subfertility due to structural and functional abnormality of the sperms
Tubal patency can be affected by diseases in the male genital tract such as sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia, gonococcal infection and genital tuberculosis. These disease conditions cause the scarring of the duct system and the scar tissues block the tubes, preventing the transportation of sperms.
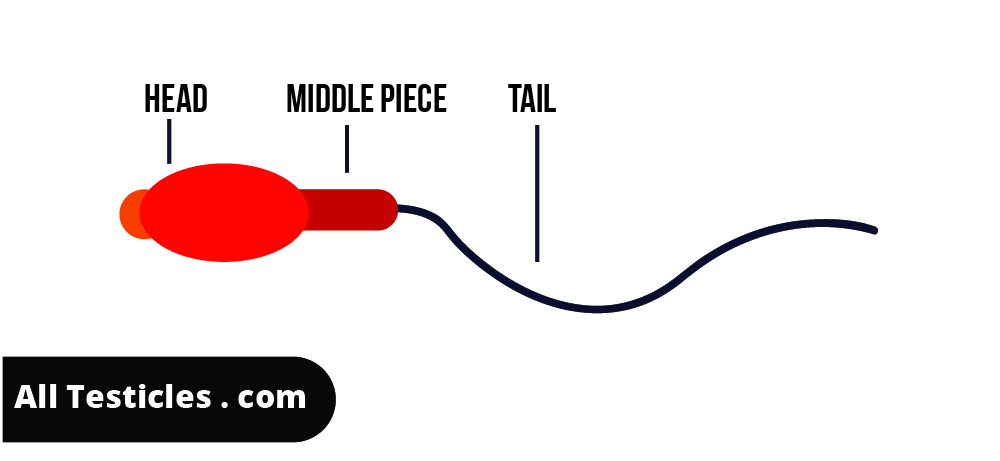
Normal sperm is consists of head, midpiece and a tail. Abnormalities of the sperms can be found in various forms. These abnormalities are,
- Giant sperms
- Micro- sperm
- Double head
- Double body etc.
Idiopathic Oligoasthenoteratozoopermia
In this condition sperm count, motility and normal form of sperms are reduced. The cause is unknown. This is the most common cause for male subfertility all around the word, but the cause remains unknown. It can be identified easily with Seminal Fluid Analysis (SFA) The name of the condition seems scary, but is very understandable once we breakdown the name.
- Oligozoospermia: Reduced sperm count
- TeratoZoospermia: Abnormal sperm shapes
- AsthenoZoospermia: Impaired sperm motility.
Other structural and functional abnormalities of the sperms occur due to,
- Alcohol abuse
- smoking
- Caffeinated beverages
- Excessive exposure to industrial chemicals
- Wearing tight under wears
- Exposure to heat
Other causes for male subfertility
Varicocele
Varicocele is another known cause of male subfertility. In a varicocele, there is an enlargement and dilation of the veins that drain blood from testicles.
One advantage of scrotum being situated outside the body is that scrotum is cooler than the internal body temperature, and its ideal for sperm production. Unfortunately in varicocele, the stagnant blood raises the scrotal temperature, thus impairing the sperm production.
What are the signs and symptoms associated with male subfertility?
Several signs and symptoms which can indicate underlying health conditions,
- Problems associated with sexual function
- Lack of sexual desire
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Lump in the testis
- Inability to smell
- Abnormally enlarged breasts
- Decrease facial or body hair
If you have any of these features, it is better to see a doctor to find the cause and get treatment.
What’s next: In the coming week, I’ll discuss about how to use Seminal Fluid Analysis to identify poor sperm quality.